What is green hydrogen?Hauwai kākāriki
Here we explain what green hydrogen is, how we can use it, and how GNS Science is working to make it affordable and accessible.
Hydrogen (chemical symbol H) is the universe’s most abundant chemical element and is readily available on Earth. It’s very light, making it easy to store and transport. It also reacts very easily with other elements, so on Earth it is usually part of more complex molecules – for example in water, as two parts hydrogen to one part oxygen (H2O), or in hydrocarbons such as oil, gas and coal.

Today = 'grey' hydrogen
Today, hydrogen is mostly used in industrial processes or as a chemical feedstock, especially in agriculture. Currently 95% of hydrogen produced globally is via steam reformation of natural gas, a highly carbon-intensive process responsible for hundreds of millions of tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions worldwide – around one percent of humanity’s entire carbon footprint. Hydrogen produced this way is often referred to as ‘grey’ hydrogen.
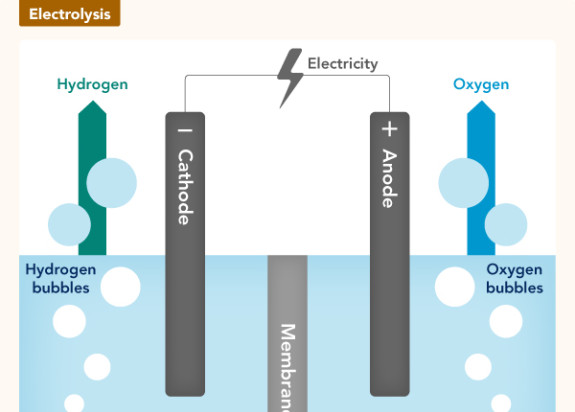
Tomorrow = a much cleaner method
Green hydrogen is a produced by a much cleaner method. Powered by renewable electricity sources (such as solar, wind or geothermal), water (H2O) is split into hydrogen and oxygen using a process known as electrolysis. It can be stored and transported as a liquid or gas.